What Does A Negative Price To Earnings Ratio Mean? A Deep Dive Into This Financial Mystery
Hey there, finance enthusiasts! Ever stumbled upon a company's financial metrics and got baffled by a negative price to earnings ratio? Yeah, it’s one of those terms that can make your head spin if you're not familiar with the lingo. Let’s break it down in simple terms. A negative price to earnings ratio, or P/E ratio, is essentially a red flag in the world of investing. It means the company is losing money, which can be a big deal depending on the context. But hold up, not all negative P/E ratios are created equal. Stick around, because we're diving deep into this topic and uncovering the secrets behind this financial mystery.
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. The price to earnings ratio is a key indicator for investors, helping them gauge whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued. When this number turns negative, it raises some eyebrows. But what exactly does it mean, and why should you care? If you're an investor or just someone curious about how businesses are evaluated, this article is for you. We'll break it down step by step so you can understand the implications of a negative P/E ratio.
Now, here’s the deal: a negative P/E ratio doesn’t automatically mean the company is doomed. Sometimes, it’s just a phase, like when a business is investing heavily in growth or restructuring. Other times, it might signal deeper issues. Either way, it’s crucial to understand the context and the factors at play. So, grab a coffee, and let’s unravel the meaning behind this financial enigma together.
Understanding the Basics of Price to Earnings Ratio
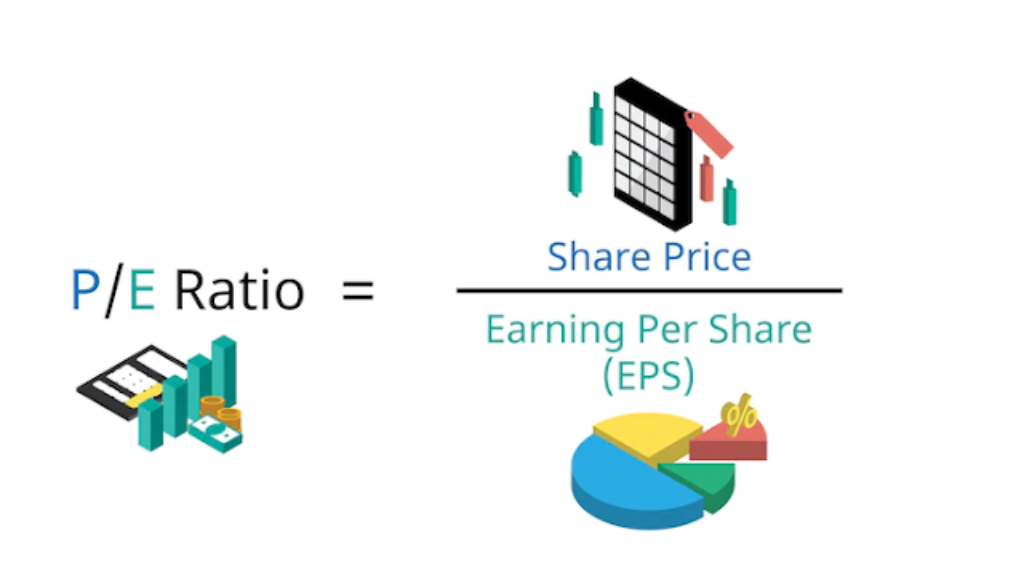
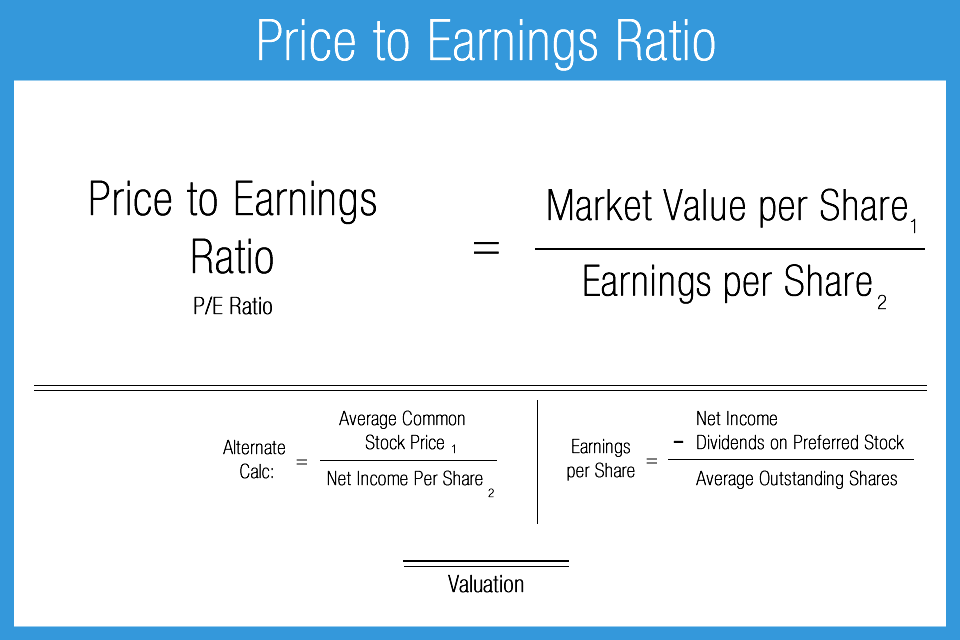
Alright, let’s rewind a bit and start with the basics. The price to earnings ratio is like the heartbeat of a company’s financial health. It’s calculated by dividing the stock price by the earnings per share (EPS). For example, if a stock is trading at $50 and the EPS is $5, the P/E ratio would be 10. Simple, right? But what happens when the earnings per share is negative? That’s where things get interesting.
Why Is the P/E Ratio Important?
The P/E ratio is like a scorecard for investors. It tells you how much you’re paying for each dollar of a company’s earnings. A high P/E ratio might indicate that investors expect strong future growth, while a low P/E ratio could suggest the stock is undervalued or the company is struggling. However, when the P/E ratio is negative, it’s like a big, flashing warning sign. It means the company is losing money, and its earnings are in the red.
What Does a Negative Price to Earnings Ratio Mean?
So, here’s the million-dollar question: what does a negative P/E ratio really mean? Simply put, it means the company is posting net losses instead of profits. The earnings per share is negative, which flips the P/E ratio into the negatives. This situation can arise for various reasons, and it’s essential to dig deeper to understand the underlying causes. Is the company just going through a rough patch, or are there more serious issues at play?
Common Causes of Negative P/E Ratios
Let’s break down some of the common reasons behind a negative P/E ratio:
- Temporary Losses: Sometimes, companies experience short-term losses due to one-time events like restructuring or legal settlements.
- Investment in Growth: A company might intentionally incur losses to invest in expansion, research, or new markets. Think of it as planting seeds for future harvests.
- Industry Challenges: Certain industries, like tech startups or biotech firms, often operate at a loss in their early stages as they focus on innovation and scaling.
- Financial Distress: In some cases, a negative P/E ratio might indicate deeper financial problems, such as declining sales or mounting debt.
Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
Not necessarily. While a negative P/E ratio can raise red flags, it’s not always a sign of doom. Some companies deliberately operate at a loss to gain market share or develop groundbreaking products. For instance, many tech giants like Amazon and Tesla spent years with negative earnings before becoming profitable. It’s all about understanding the company’s strategy and long-term prospects.
When Is a Negative P/E Ratio Acceptable?
Here are a few scenarios where a negative P/E ratio might be acceptable:
- High-Growth Companies: Startups and growth-stage companies often prioritize expansion over immediate profitability.
- Strategic Investments: Companies investing heavily in R&D or infrastructure might report losses in the short term.
- Market Disruptions: In rapidly evolving industries, companies might sacrifice profits to stay competitive.
How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
Interpreting a negative P/E ratio requires more than just looking at the numbers. You need to consider the broader context, including the company’s business model, industry trends, and management strategy. For example, a biotech firm with a negative P/E ratio might be on the verge of launching a life-changing drug, while a retail company with the same ratio might be struggling to adapt to e-commerce.
Key Factors to Consider
When analyzing a negative P/E ratio, keep these factors in mind:
- Revenue Growth: Is the company generating steady revenue despite its losses?
- Cash Flow: Does the company have enough cash reserves to sustain operations?
- Management Quality: Are the leaders making sound decisions to turn things around?
- Market Sentiment: How are investors and analysts reacting to the company’s performance?
Examples of Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
To better understand the concept, let’s look at some real-world examples. Companies like Tesla, Shopify, and Beyond Meat have all experienced negative P/E ratios during their growth phases. These firms chose to prioritize market penetration and innovation over immediate profitability, and it paid off in the long run. On the flip side, some companies with negative P/E ratios have struggled to recover, highlighting the risks involved.
Case Study: Tesla
Tesla is a classic example of a company that operated with a negative P/E ratio for years. Despite posting losses, the company continued to invest in cutting-edge technology and expand its product lineup. Investors believed in its vision, and their patience eventually paid off as Tesla became one of the most valuable automakers in the world.
Investor Implications of a Negative P/E Ratio
For investors, a negative P/E ratio can be both a warning sign and an opportunity. It’s crucial to assess the company’s fundamentals and long-term potential before making any decisions. Some investors might see it as a chance to buy undervalued stocks, while others might steer clear due to the associated risks.
Risk vs. Reward
Here’s how to weigh the risks and rewards:
- Risk: The company might fail to turn a profit, leading to further losses or even bankruptcy.
- Reward: If the company succeeds in its growth strategy, the returns could be substantial.
How to Analyze Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
Now that you know what a negative P/E ratio means, let’s talk about how to analyze these companies effectively. Start by examining their financial statements, revenue trends, and cash flow. Look for signs of improvement, such as increasing sales or decreasing losses. Additionally, pay attention to industry dynamics and competitive positioning.
Tools and Resources
Here are some tools and resources to help you analyze companies with negative P/E ratios:
- Financial Statements: Review the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- Analyst Reports: Read insights from industry experts and analysts.
- News Updates: Stay informed about the latest developments affecting the company.
Conclusion: What Should You Do Next?
In conclusion, a negative price to earnings ratio is not the end of the world. It’s a signal to dig deeper and understand the underlying reasons behind the losses. Some companies use this phase to build a strong foundation for future success, while others might struggle to recover. As an investor, it’s up to you to evaluate the risks and opportunities before making any decisions.
So, what’s next? If you’re intrigued by this topic, why not share your thoughts in the comments below? Or better yet, check out some of our other articles on financial metrics and investment strategies. Remember, knowledge is power, and the more you learn, the better equipped you’ll be to navigate the world of finance.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of Price to Earnings Ratio
- What Does a Negative Price to Earnings Ratio Mean?
- Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
- How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
- Examples of Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
- Investor Implications of a Negative P/E Ratio
- How to Analyze Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
- Conclusion: What Should You Do Next?