ROCE Vs ROE: Which Financial Metric Reigns Supreme In The World Of Business?
Let’s cut straight to the chase. When it comes to analyzing a company's financial health, ROCE and ROE are two big players in the game. If you’re scratching your head wondering what these acronyms mean, don’t worry—you’re not alone. These terms might sound like alphabet soup, but they’re actually critical tools for investors, analysts, and business owners alike. Understanding the difference between ROCE vs ROE can help you make smarter financial decisions and assess a company's profitability like a pro.
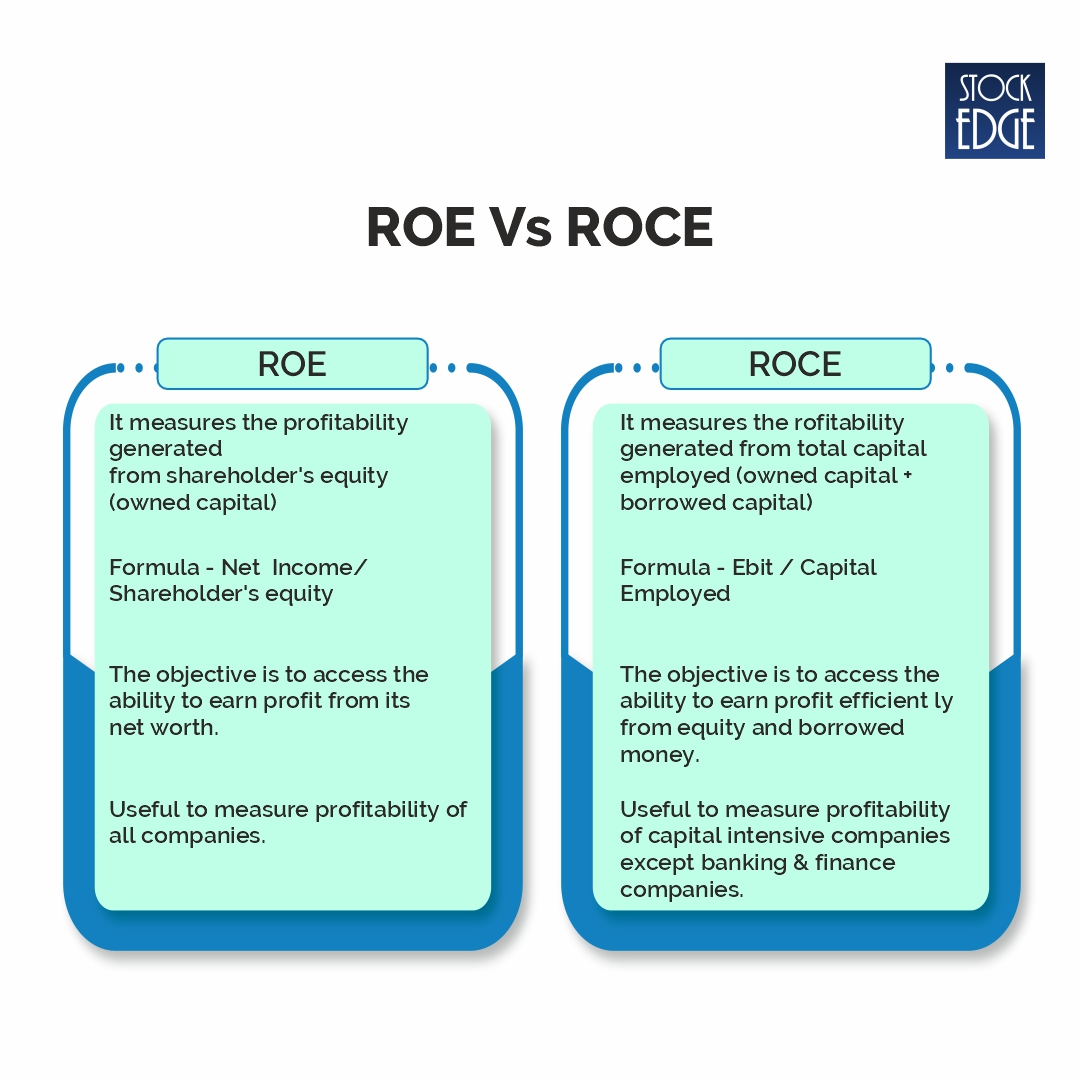
Think of it this way: If a company is a car, ROCE and ROE are the gauges that tell you how well the engine is running. ROCE (Return on Capital Employed) measures how efficiently a company uses its capital to generate profits. Meanwhile, ROE (Return on Equity) focuses on how effectively a company uses shareholders’ equity to produce returns. Both metrics give you a snapshot of a company’s financial performance, but they do it from slightly different angles.
Now, why should you care? Well, whether you're an investor looking for the next big stock or a business owner wanting to maximize profits, understanding these metrics can be a game-changer. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of ROCE vs ROE, break down their differences, and show you how to use them to make informed decisions. So buckle up and get ready to level up your financial IQ!
What is ROCE? A Quick Primer
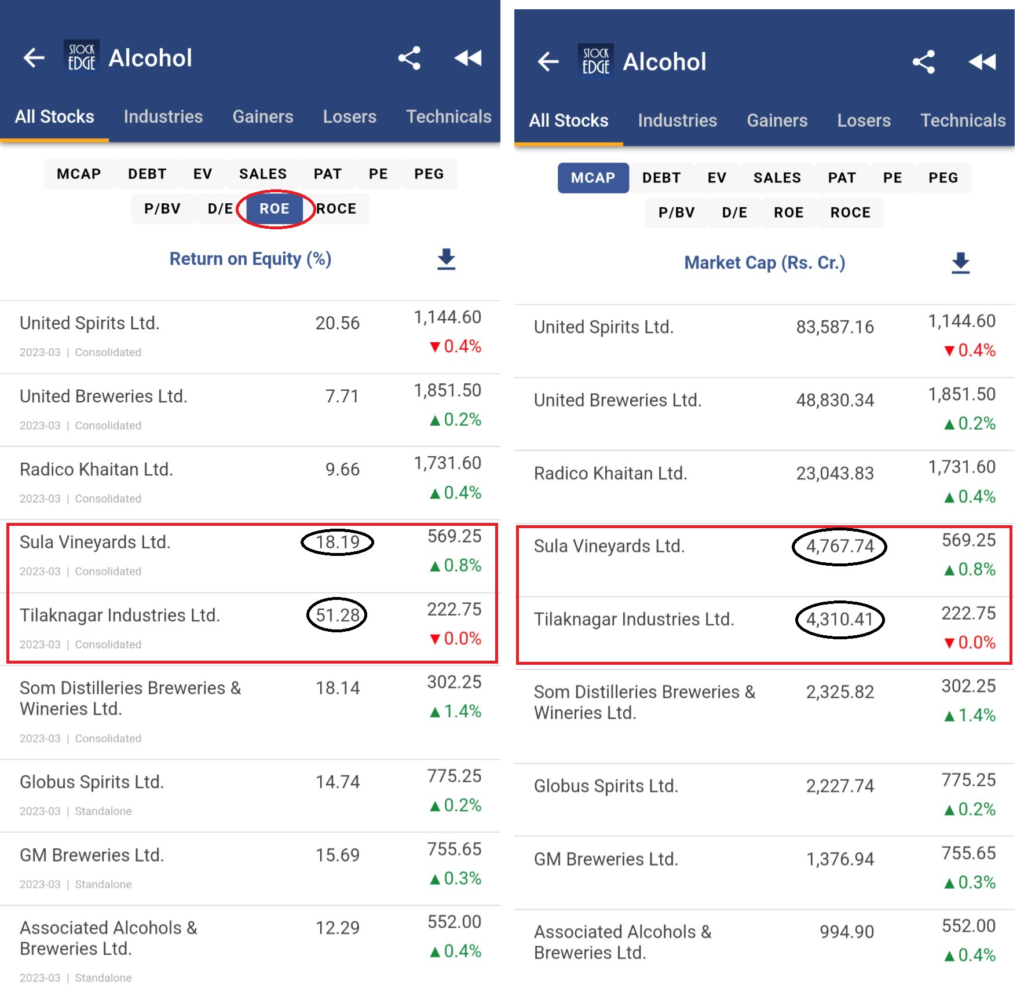
ROCE, or Return on Capital Employed, is like the Swiss Army knife of financial metrics. It tells you how well a company is using its capital—both debt and equity—to generate profits. In simpler terms, it shows you how much bang you’re getting for your buck. The formula for ROCE is pretty straightforward: EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) divided by Capital Employed. But don’t let the math scare you—it’s easier than it sounds.
For example, imagine a company has an EBIT of $100,000 and capital employed of $500,000. Their ROCE would be 20%. Not bad, right? But here’s the kicker: A high ROCE doesn’t always mean a company is doing great. You’ve got to look at it in context, comparing it to industry standards and historical performance. That’s where things get interesting.
Why ROCE Matters
ROCE is a favorite among analysts because it gives a holistic view of a company’s operations. Unlike some other metrics, it takes into account both debt and equity, giving you a more complete picture of how a company is financed. Plus, it’s not as easily manipulated by accounting tricks, which makes it a reliable indicator of long-term performance.
- ROCE helps you gauge operational efficiency.
- It’s especially useful for comparing companies within the same industry.
- High ROCE usually signals strong management and smart capital allocation.
But here’s the thing: ROCE isn’t perfect. It doesn’t account for things like market conditions or one-time gains, which can skew the numbers. That’s why it’s always a good idea to pair it with other metrics—like ROE, for instance.
ROE: The Shareholder’s Best Friend
Now let’s talk about ROE, or Return on Equity. This metric is all about the shareholders. It measures how effectively a company uses the money invested by its owners to generate profits. The formula is simple: Net Income divided by Shareholders’ Equity. It’s like asking, “How much am I getting back for every dollar I put in?”
For example, if a company has a net income of $50,000 and shareholders’ equity of $250,000, its ROE would be 20%. Sounds familiar, right? That’s because ROE and ROCE often overlap, but they focus on different aspects of a company’s financial health.
Key Benefits of ROE
ROE is a go-to metric for investors because it directly ties profitability to equity. Here’s why it matters:
- It shows how well a company is rewarding its shareholders.
- Higher ROE usually means better returns for investors.
- It’s a great way to compare companies, especially in capital-intensive industries.
But here’s the catch: ROE can be misleading if a company uses a lot of debt to finance its operations. In that case, the equity base might be smaller, making the ROE look artificially high. That’s why it’s important to look at ROE alongside other metrics—like, you guessed it, ROCE.
ROCE vs ROE: The Battle of the Metrics
Alright, let’s get to the main event. ROCE vs ROE: Who comes out on top? The answer, as you might expect, depends on what you’re looking for. ROCE gives you a broader view of a company’s financial health, while ROE zeroes in on shareholder returns. Both have their strengths and weaknesses, so it’s not really a matter of one being better than the other—it’s about using them together to get the full picture.
Here’s a quick breakdown:
- ROCE is great for analyzing operational efficiency and capital management.
- ROE is perfect for assessing shareholder value and return on investment.
- Together, they provide a more complete understanding of a company’s financial performance.
When to Use ROCE
If you’re trying to figure out how efficiently a company is using its capital, ROCE is your go-to metric. It’s especially useful for comparing companies within the same industry, where capital structure might vary. For example, a manufacturing company might have a lot of fixed assets, while a tech company might rely more on intellectual property. ROCE helps level the playing field by focusing on how well each company uses its resources.
When to Use ROE
On the other hand, if you’re an investor looking for the best bang for your buck, ROE is your best friend. It tells you how much profit you’re getting for every dollar you invest. Just remember to consider the company’s debt levels—too much leverage can make ROE look better than it really is.
Industry Insights: How ROCE and ROE Play Out
Now, let’s take a look at how ROCE and ROE play out in different industries. In capital-intensive sectors like manufacturing or utilities, ROCE tends to be more important because these companies rely heavily on fixed assets. A high ROCE in these industries usually signals strong operational efficiency and smart capital allocation.
In contrast, in industries like tech or finance, ROE might take center stage. These companies often have lower capital requirements and higher equity bases, making ROE a better indicator of profitability. For example, a software company might have a high ROE because it doesn’t need a lot of physical assets to generate profits.
Case Study: Tech vs Manufacturing
Let’s say you’re comparing two companies: one in tech and one in manufacturing. The tech company might have an ROE of 30% and a ROCE of 20%, while the manufacturing company has an ROE of 15% and a ROCE of 25%. At first glance, the tech company seems like the better investment, right? But hold on—when you look at the big picture, the manufacturing company might actually be more efficient at using its capital, even if its ROE is lower.
Common Misconceptions About ROCE and ROE
There are a few myths floating around about ROCE and ROE that can trip you up if you’re not careful. One common misconception is that a higher ROE always means a better investment. While it’s true that high ROE can be a good sign, it doesn’t tell the whole story. A company with a lot of debt might have an artificially high ROE, which can be risky for investors.
Another myth is that ROCE is only useful for large, established companies. Not true! ROCE can be just as valuable for small businesses and startups, especially when it comes to assessing operational efficiency and capital management.
How to Avoid Pitfalls
Here are a few tips to help you avoid common pitfalls when using ROCE and ROE:
- Always consider the company’s debt levels when looking at ROE.
- Use ROCE to get a broader view of a company’s financial health.
- Compare metrics within the same industry for the most accurate insights.
Data and Statistics: The Numbers Don’t Lie
Let’s talk numbers. According to a study by McKinsey, companies with consistently high ROCE tend to outperform their peers in terms of long-term growth and profitability. Another report by Harvard Business Review found that companies with high ROE often attract more investors, but warned that excessive leverage can lead to financial instability.
But here’s the kicker: A study by the Financial Times showed that companies with a balanced approach to ROCE and ROE—using both metrics together—tend to perform the best over time. It’s like having two tools in your toolbox instead of just one.
Real-World Examples
Take Apple, for instance. The tech giant has consistently high ROE and ROCE, which has helped it maintain its position as one of the world’s most valuable companies. On the other hand, a company like General Motors might have lower ROE but higher ROCE, reflecting its capital-intensive business model.
Expert Opinions: What the Pros Say
Experts in the field agree that ROCE and ROE are powerful tools when used together. According to Warren Buffett, one of the greatest investors of all time, “A good business delivers high ROE and ROCE over time.” Buffett himself uses these metrics to evaluate potential investments, looking for companies that can sustain high returns without taking on too much debt.
Another guru, Peter Lynch, emphasizes the importance of understanding a company’s financials before investing. “Know what you own, and know why you own it,” he says. Both ROCE and ROE can help you do just that.
Why Trustworthiness Matters
When it comes to financial metrics, trustworthiness is key. That’s why it’s important to use reputable sources and avoid relying on one metric alone. By combining ROCE and ROE with other tools, you can get a more complete picture of a company’s financial health.
Conclusion: The Final Verdict
So, what’s the final verdict on ROCE vs ROE? The truth is, neither one is better than the other—they’re just different tools for different jobs. ROCE gives you a broad view of a company’s operational efficiency, while ROE focuses on shareholder returns. Together, they provide a powerful way to assess a company’s financial health and make informed decisions.
Here’s a quick recap:
- ROCE measures how efficiently a company uses its capital.
- ROE measures how effectively a company uses shareholders’ equity.
- Both metrics are important for analyzing financial performance.
Now it’s your turn. Whether you’re an investor, analyst, or business owner, understanding ROCE vs ROE can help you make smarter decisions. So take what you’ve learned and put it into practice. And don’t forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues—knowledge is power, after all!
Table of Contents
- ROCE vs ROE: Which Financial Metric Reigns Supreme in the World of Business?
- What is ROCE? A Quick Primer
- Why ROCE Matters
- ROE: The Shareholder’s Best Friend
- Key Benefits of ROE
- ROCE vs ROE: The Battle of the Metrics
- When to Use ROCE
- When to Use ROE
- Industry Insights: How ROCE and ROE Play Out
- Case Study: Tech vs Manufacturing
- Common Misconceptions About ROCE and ROE
- How to Avoid Pitfalls
- Data and Statistics: The Numbers Don’t Lie
- Real-World Examples
- Expert Opinions: What the Pros Say
- Why Trustworth