What Is The Difference Between Stakeholder And Shareholder: A Clear Breakdown
Ever wondered what sets stakeholders apart from shareholders? If you're diving into the world of business, finance, or management, these terms are more than just buzzwords—they're essential concepts that shape how organizations operate. Whether you're a student, entrepreneur, or simply curious about the business landscape, understanding the difference between stakeholders and shareholders is key to grasping how companies work and who holds the power. So, buckle up and let's break it down!
In today's fast-paced business environment, the terms "stakeholder" and "shareholder" often get thrown around like synonyms. But here's the kicker—they're not the same thing. While both groups have an interest in a company's performance, their roles, priorities, and influence differ significantly. Knowing these distinctions can help you navigate the business world with confidence.
As we dive deeper into this topic, you'll discover the nuances of each term, the roles they play, and why it matters. By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of what makes stakeholders and shareholders unique. And who knows? You might even impress your friends at your next dinner party with your newfound business savvy!
Defining Stakeholders and Shareholders
Let's start with the basics. To truly grasp the difference between stakeholders and shareholders, we need to define each term clearly. Think of them as two sides of the same coin, but with distinct characteristics that set them apart.
Who Are Stakeholders?
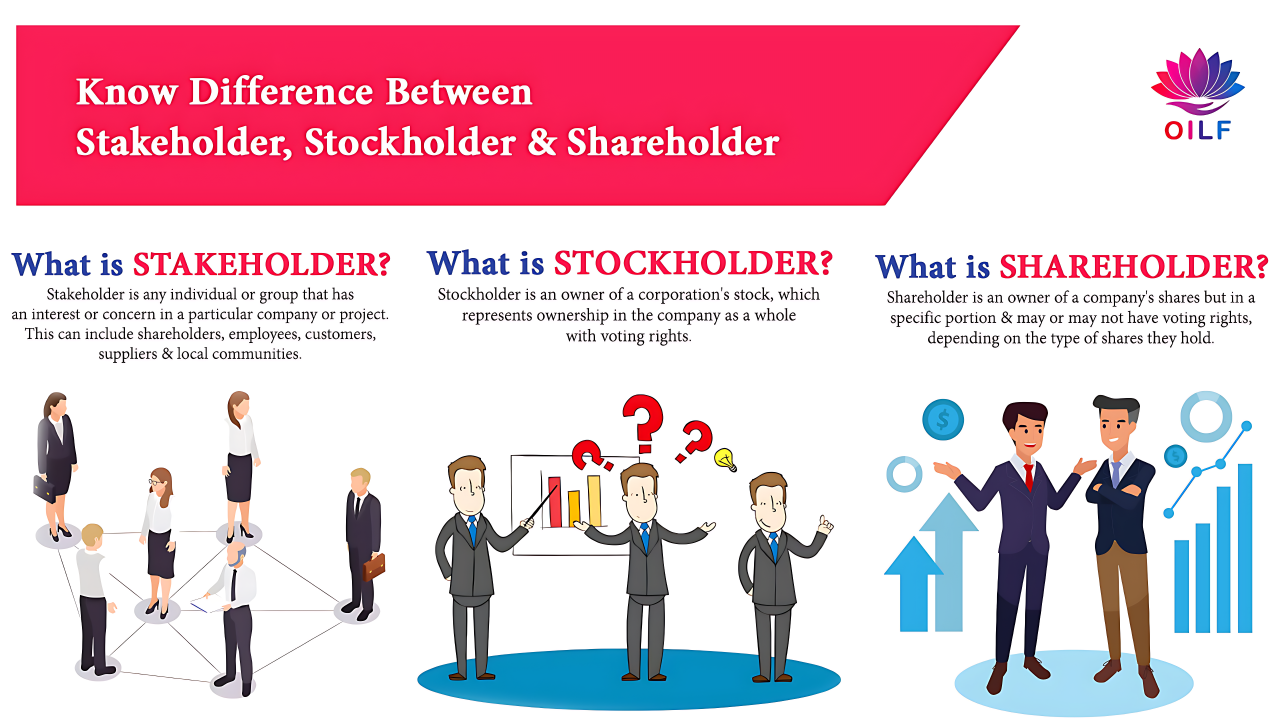
Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest in a company's performance. This interest can be financial, social, or environmental. In other words, stakeholders are anyone who is affected by or can affect a company's actions. This broad definition means that stakeholders can include employees, customers, suppliers, local communities, and even the government.
- Employees rely on the company for their livelihood.
- Customers depend on the company for products or services.
- Suppliers need the company as a buyer for their goods.
- Local communities may benefit from the company's presence through job creation or infrastructure development.
Who Are Shareholders?
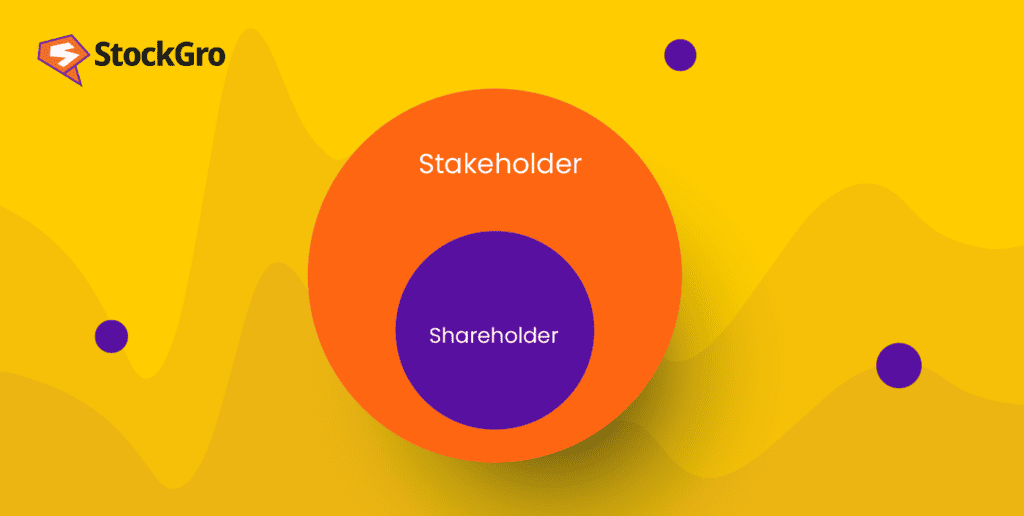
Shareholders, on the other hand, are a specific type of stakeholder. They are individuals or entities who own shares in a company. By purchasing stock, shareholders become partial owners of the company and have a financial stake in its success. Their primary interest lies in maximizing their return on investment, which is typically achieved through dividends or stock appreciation.
- Shareholders have voting rights in certain company decisions.
- They receive financial benefits when the company performs well.
- Unlike other stakeholders, their interest is primarily monetary.
Key Differences Between Stakeholders and Shareholders
Now that we've defined both terms, let's highlight the key differences between stakeholders and shareholders. These distinctions are crucial for understanding their roles in a company's ecosystem.
Scope of Interest
Stakeholders have a wide range of interests that go beyond financial gain. They care about the company's impact on society, the environment, and the economy. Shareholders, however, focus primarily on financial returns. Their interest is narrower and more specific.
Level of Influence
While both stakeholders and shareholders can influence a company's decisions, their power varies. Shareholders wield significant influence through voting rights and ownership stakes. Stakeholders, especially those without financial ties, may have less direct power but can still impact a company through public opinion, boycotts, or advocacy.
Financial Involvement
Shareholders invest money in a company by purchasing shares, making them direct financial contributors. Stakeholders, however, may not have any financial stake in the company. Their involvement is often indirect, such as through employment, consumption of products, or community engagement.
Types of Stakeholders
Not all stakeholders are created equal. Depending on their relationship with the company, stakeholders can be categorized into different types. Understanding these categories helps businesses tailor their strategies to meet the needs of various groups.
Internal Stakeholders
Internal stakeholders are those who work within the company. This includes employees, managers, and executives. Their interests are closely tied to the company's success, as their jobs and livelihoods depend on it.
External Stakeholders
External stakeholders are those outside the company who are impacted by its activities. This group includes customers, suppliers, investors, and the local community. Each subgroup has unique needs and expectations that companies must address.
The Role of Shareholders
Shareholders play a vital role in a company's governance and financial health. Their influence extends beyond owning shares; they also participate in decision-making processes and hold companies accountable for their performance.
Voting Rights
One of the most significant powers shareholders have is their voting rights. They can vote on critical issues such as electing board members, approving mergers, and making major financial decisions. This democratic process ensures that shareholders have a say in how the company is run.
Financial Contributions
By purchasing shares, shareholders provide the capital that companies need to grow and expand. Their financial contributions are essential for funding research and development, launching new products, and entering new markets.
Why the Distinction Matters
Understanding the difference between stakeholders and shareholders is more than just academic; it has practical implications for businesses and society as a whole. Companies that fail to recognize these distinctions risk alienating important groups and jeopardizing their long-term success.
Corporate Social Responsibility
In today's world, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a hot topic. Companies are increasingly expected to consider the needs of all stakeholders, not just shareholders. This shift reflects a growing awareness of the broader impact businesses have on society and the environment.
Strategic Planning
By distinguishing between stakeholders and shareholders, companies can develop more effective strategies. For example, they can prioritize initiatives that benefit both groups, such as sustainable practices that appeal to environmentally conscious stakeholders while also improving long-term profitability for shareholders.
How Stakeholders and Shareholders Interact
The relationship between stakeholders and shareholders is complex and dynamic. While they may have different priorities, they often find themselves working together to achieve common goals. This collaboration can lead to innovative solutions and mutual benefits.
Communication
Effective communication is key to bridging the gap between stakeholders and shareholders. Companies that engage in transparent dialogue with both groups can build trust and foster collaboration. Regular updates, town hall meetings, and feedback sessions are just a few ways to keep everyone informed and engaged.
Conflict Resolution
Of course, conflicts can arise when stakeholders and shareholders have competing interests. For example, a decision that benefits shareholders might harm employees or the local community. In such cases, companies must navigate these challenges carefully, balancing short-term gains with long-term sustainability.
Data and Statistics on Stakeholders and Shareholders
To put things into perspective, let's look at some data and statistics that highlight the importance of stakeholders and shareholders in the business world.
- According to a 2022 survey, 77% of consumers consider a company's social and environmental impact when making purchasing decisions.
- In the same year, global stock markets saw a record $10 trillion in equity investments, underscoring the significance of shareholders in the financial ecosystem.
- Companies with strong stakeholder engagement tend to outperform their peers by an average of 18% in terms of stock performance.
Expert Insights on Stakeholder vs. Shareholder
To gain a deeper understanding of this topic, we turned to industry experts for their perspectives. Their insights shed light on the evolving landscape of business and the growing importance of stakeholder management.
Dr. Jane Thompson, a renowned business professor, notes, "The traditional focus on shareholders is giving way to a more holistic approach that considers the needs of all stakeholders. This shift reflects a broader recognition of the interconnectedness of business and society."
Conclusion: Embracing the Difference
In conclusion, the difference between stakeholders and shareholders is both subtle and profound. While shareholders are a specific type of stakeholder with financial interests, stakeholders encompass a broader range of groups with diverse concerns. Understanding these distinctions is essential for businesses that want to thrive in today's complex and interconnected world.
We invite you to join the conversation by sharing your thoughts in the comments below. Do you think companies are doing enough to balance the needs of stakeholders and shareholders? What steps can they take to improve? Your input matters, and we'd love to hear from you!
Table of Contents
- Defining Stakeholders and Shareholders
- Key Differences Between Stakeholders and Shareholders
- Types of Stakeholders
- The Role of Shareholders
- Why the Distinction Matters
- How Stakeholders and Shareholders Interact
- Data and Statistics on Stakeholders and Shareholders
- Expert Insights on Stakeholder vs. Shareholder
- Conclusion: Embracing the Difference