P/E Ratio Is Negative: What Does It Mean For Your Investment?
Imagine this: you're scrolling through stock reports, trying to figure out which company to invest in. You come across a stock with a negative P/E ratio, and suddenly your brain goes into overdrive. What does it mean? Is it a good thing or a disaster waiting to happen? Don’t panic! We’ve all been there. Understanding why a P/E ratio is negative and what it signifies is crucial before jumping into any investment decision.
A negative P/E ratio isn’t as scary as it sounds, but it definitely raises some red flags. For investors, this number can be confusing, especially if you’re new to the stock market game. But here’s the deal: sometimes a negative P/E ratio isn’t necessarily bad—it just means you need to dig a little deeper. In this article, we’ll break it down for you, no fancy jargon included.
So, why is the P/E ratio important? Well, it’s one of the most commonly used metrics to evaluate a company’s stock. It helps you understand whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued compared to its earnings. But when that number dips into the negatives, it’s time to pay attention. Let’s dive in and figure out what’s really going on.
What is a P/E Ratio?
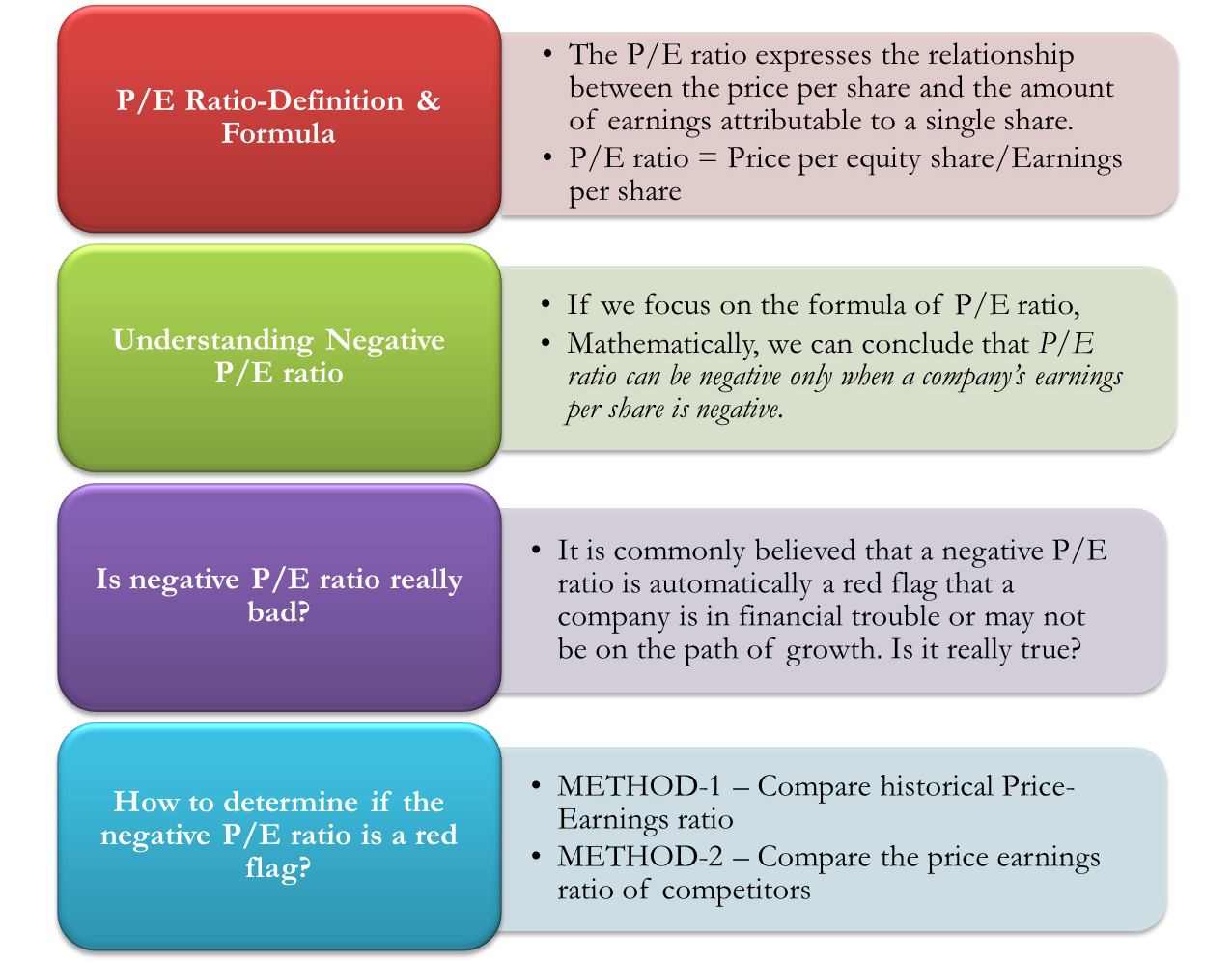
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of a negative P/E ratio, let’s first talk about what a P/E ratio actually is. The P/E ratio, short for Price-to-Earnings ratio, is a way to measure how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. It’s calculated by dividing the stock price by the company’s earnings per share (EPS).
Here’s the basic formula:
P/E Ratio = Stock Price ÷ Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Now, here’s the kicker: the P/E ratio is like a report card for a company’s financial health. A high P/E ratio might mean the stock is overpriced, while a low P/E ratio could indicate it’s undervalued. But what happens when the P/E ratio goes negative? That’s where things get interesting.
Why Can a P/E Ratio Be Negative?
Alright, so we know what a P/E ratio is, but why does it turn negative? The answer is pretty simple: it happens when a company reports negative earnings. Yep, you heard that right. If a company is losing money instead of making profits, its earnings per share (EPS) will be negative, and that’s what causes the P/E ratio to flip into the negatives.
Let’s break it down:
- A company’s earnings are negative because it’s operating at a loss.
- When you divide the stock price by a negative EPS, you get a negative P/E ratio.
This doesn’t necessarily mean the company is doomed, but it does signal that something’s not quite right. Maybe the company’s going through a rough patch, or it’s investing heavily in growth opportunities that haven’t paid off yet. Either way, it’s a sign that you need to investigate further.
Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
Here’s the million-dollar question: is a negative P/E ratio always a bad thing? Not necessarily. While it can be a warning sign, it’s not always the end of the world. Sometimes, companies report negative earnings temporarily because they’re investing in long-term growth strategies. Think about it: would you rather invest in a company that’s making small profits now or one that’s setting itself up for massive growth in the future?
Let’s look at some scenarios:
- Temporary Losses: The company might be experiencing short-term losses due to market conditions or one-time expenses.
- Expansion Phase: It could be investing heavily in new markets, technology, or products, which might lead to losses in the short term but big gains in the long run.
- Industry Challenges: Certain industries, like startups or biotech companies, often operate at a loss initially because they require significant upfront investment.
So, while a negative P/E ratio isn’t ideal, it doesn’t automatically mean the company is a bad investment. It just means you need to look beyond the numbers and understand the bigger picture.
Understanding the Context
When you see a negative P/E ratio, the first thing you should do is dig into the company’s financial statements. Look for patterns in their earnings reports, cash flow statements, and balance sheets. Are they consistently losing money, or is this a one-time thing? Are they reinvesting their losses into growth opportunities, or are they bleeding cash without a clear plan?
Here are some questions to ask yourself:
- Is the company in a growth phase?
- Are their losses temporary or structural?
- Do they have a solid business model and competitive advantage?
By answering these questions, you’ll get a clearer picture of whether the negative P/E ratio is a red flag or just a bump in the road.
How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
Now that we’ve established what a negative P/E ratio means, let’s talk about how to interpret it. Here’s the deal: a negative P/E ratio doesn’t tell you much on its own. You need to look at it in the context of the company’s overall financial health and industry trends.
Here are some things to consider:
- Compare to Peers: How does the company’s financial performance compare to its competitors? Are they all losing money, or is this company an outlier?
- Historical Performance: Look at the company’s earnings history. Have they been profitable in the past, or is this the first time they’re reporting losses?
- Market Conditions: Are external factors, like economic downturns or regulatory changes, affecting the company’s earnings?
Remember, a negative P/E ratio is just one piece of the puzzle. You need to look at the bigger picture to make an informed decision.
When to Walk Away
Of course, there are times when a negative P/E ratio is a clear warning sign. If a company has been consistently losing money for years without a clear plan to turn things around, it might be time to walk away. Here are some red flags to watch out for:
- Declining revenue and cash flow
- Lack of a solid business model
- High debt levels with no plan to reduce them
- Persistent negative earnings with no signs of improvement
If you see these signs, it might be best to steer clear and look for more stable investment opportunities.
Real-World Examples of Negative P/E Ratios
To help you understand how a negative P/E ratio plays out in real life, let’s look at some examples. One famous example is Tesla. Back in the early 2010s, Tesla had a negative P/E ratio because it was investing heavily in research and development for its electric vehicles. At the time, many investors were skeptical, but those who stuck with the company saw massive returns as it became one of the most valuable automakers in the world.
Another example is biotech companies. Many biotech firms operate at a loss for years while they develop new drugs. While their P/E ratios might be negative, they often have strong pipelines of potential blockbuster drugs that could lead to huge profits in the future.
These examples show that a negative P/E ratio isn’t always a dealbreaker. It just means you need to do your homework and understand the company’s long-term potential.
Lessons from Tesla and Biotech
What can we learn from these examples? First, don’t judge a company solely by its P/E ratio. Second, take the time to understand the industry and the company’s business model. And third, be patient. Sometimes the best investments take time to pay off.
How to Use P/E Ratios in Your Investment Strategy
Now that you understand what a negative P/E ratio means, how can you use this information in your investment strategy? Here are some tips:
- Use it as a Starting Point: The P/E ratio is just one metric to consider. Don’t make investment decisions based on it alone.
- Look at Other Metrics: Consider other financial metrics like revenue growth, cash flow, and debt levels to get a more complete picture.
- Do Your Research: Read the company’s financial statements, analyst reports, and industry news to understand the context behind the numbers.
By combining the P/E ratio with other tools, you’ll be able to make more informed investment decisions.
Final Thoughts: Should You Invest in a Stock with a Negative P/E Ratio?
So, should you invest in a stock with a negative P/E ratio? The answer, as always, is it depends. If the company has a solid business model, a clear path to profitability, and strong growth potential, it might be worth considering. But if the company is bleeding cash with no plan to stop, it’s probably best to steer clear.
Remember, investing is all about balancing risk and reward. A negative P/E ratio doesn’t automatically mean a company is a bad investment, but it does mean you need to do your homework. Take the time to understand the company’s financial health, industry trends, and long-term prospects before making any decisions.
And here’s a little call to action for you: if you’ve found this article helpful, drop a comment below and let us know what you think. Are there any other investment topics you’d like us to cover? Share this article with your friends and family, and don’t forget to check out our other articles for more investing tips and tricks. Happy investing, and may the odds be ever in your favor!
Table of Contents
- What is a P/E Ratio?
- Why Can a P/E Ratio Be Negative?
- Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
- Understanding the Context
- How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
- When to Walk Away
- Real-World Examples of Negative P/E Ratios
- Lessons from Tesla and Biotech
- How to Use P/E Ratios in Your Investment Strategy
- Final Thoughts: Should You Invest in a Stock with a Negative P/E Ratio?